吉林大学课题组近日在岩土工程学术期刊《Engineering Geology》发表了题为“Differential freezing behavior of different pore water types in saline soil and its influence on soil dynamic characteristics”(盐渍土中不同类型孔隙水的差异性冻结行为及其对土体动力特性的影响)的学术文章。本研究综合采用核磁共振仪、动三轴试验系统及可控降温平台,对中国东北三种含水率盐渍土中自由水、毛细水与结合水的差异化冻结过程进行精细监测,提出四阶段冻结模型,系统揭示孔隙冰类型-结构-力学耦合机制,证实冰饱和度升高将指数级放大动剪切模量与动弹性模量,为寒区工程安全评价提供理论依据。
*论文版权归原作者和出版方所有,本文仅为学习交流。
以下是对这项成果的简要介绍:
论文摘要
不同类型水分(自由水、毛细水和结合水)的差异性冻结行为,决定了孔隙冰骨架形态的演化及其结构完整性,进而影响冻土的冻结强度。本研究采用来自中国东北地区的三种含水率盐渍土,结合降温法、核磁共振技术和动三轴试验系统,表征了不同类型孔隙水的差异性冻结过程及其对土体动力学特性的影响。研究确定了两个T2截止值:3 ms用于区分毛细水与结合水,33 ms用于区分结合水与自由水。基于自由水与结合水的冻结温度与速率,提出了一种创新的四阶段冻结模型,包括:过冷阶段(阶段I,0 °C ∼ Tf)、自由水冻结阶段(阶段II,Tf ∼ −3 °C)、结合水快速冻结阶段(阶段III,Tb ∼ −6 °C)以及结合水稳定冻结阶段(阶段IV,< −6 °C)。自由水冻结形成离散的承载冰,可显著提高土体的动剪切模量(Gd);结合水快速冻结生成结构性冰,主要提升动弹性模量(Ed);而结合水的稳定冻结则进一步增强冰骨架的结构完整性。孔隙冰对土体动力特性的增强效应随冰饱和度(ice saturation)的增加呈指数增长。该研究成果为评估盐渍冻土区既有工程设施的运行性能提供了理论依据,并为应对气候变暖背景下冻土承载力可能下降而制定新的安全标准提供了支持。
试验设备
本研究使用了GDS温控动三轴试验系统ELDYN等设备。
GDS标准型动态三轴试验系统 (ELDYN)是一种基于带电机驱动器的轴向刚性加载架的三轴系统。ELDYN可以满足室内岩土试验领域对动三轴实验系统低成本、功能全的要求,同时仍然满足客户对GDS的高标准期望。
相关图表
*图表为论文截图,版权归论文原作者和出版方所有,本文仅为学习交流。
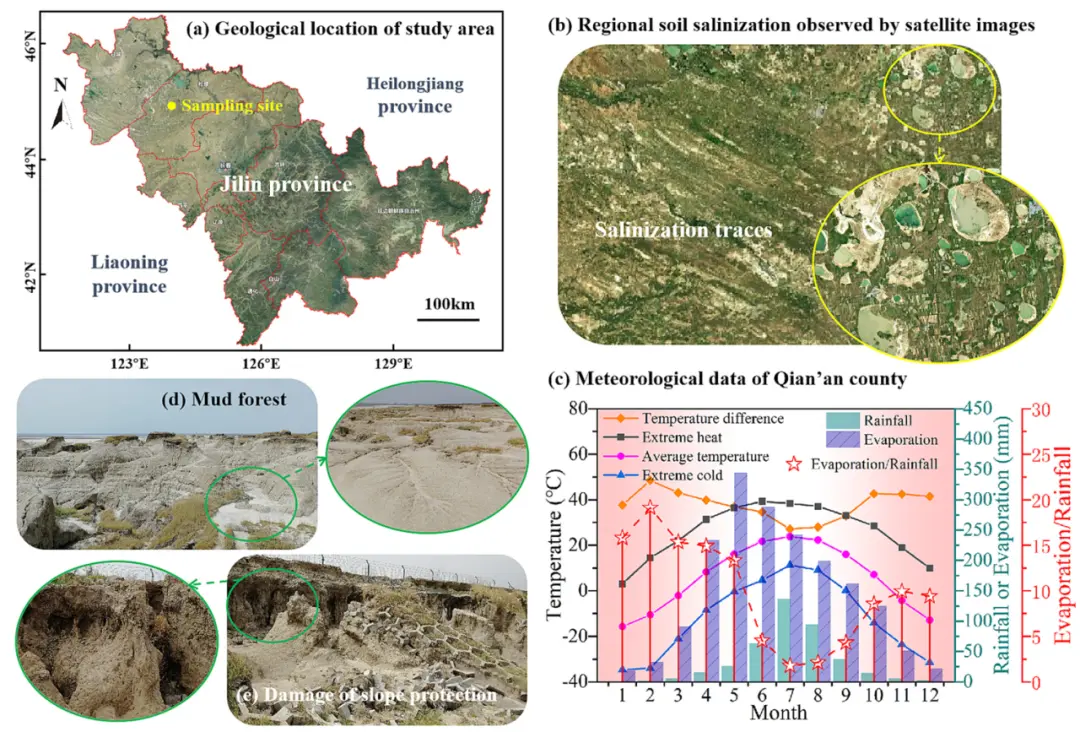
Fig. 1. (a) Geological location of study area; (b) regional soil salinization observed by satellite images; (c) meteorological data of Qian'an county; (d) mud forest landscape; (e) damage to slope protection of the open water channel.
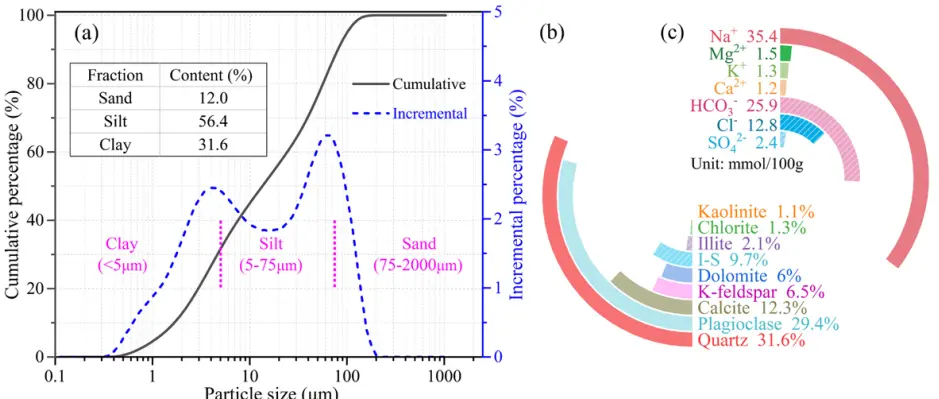
Fig. 2. Characterization of tested saline soil samples: (a) particle size distribution curve; (b) mineral composition; (c) soluble ion components.
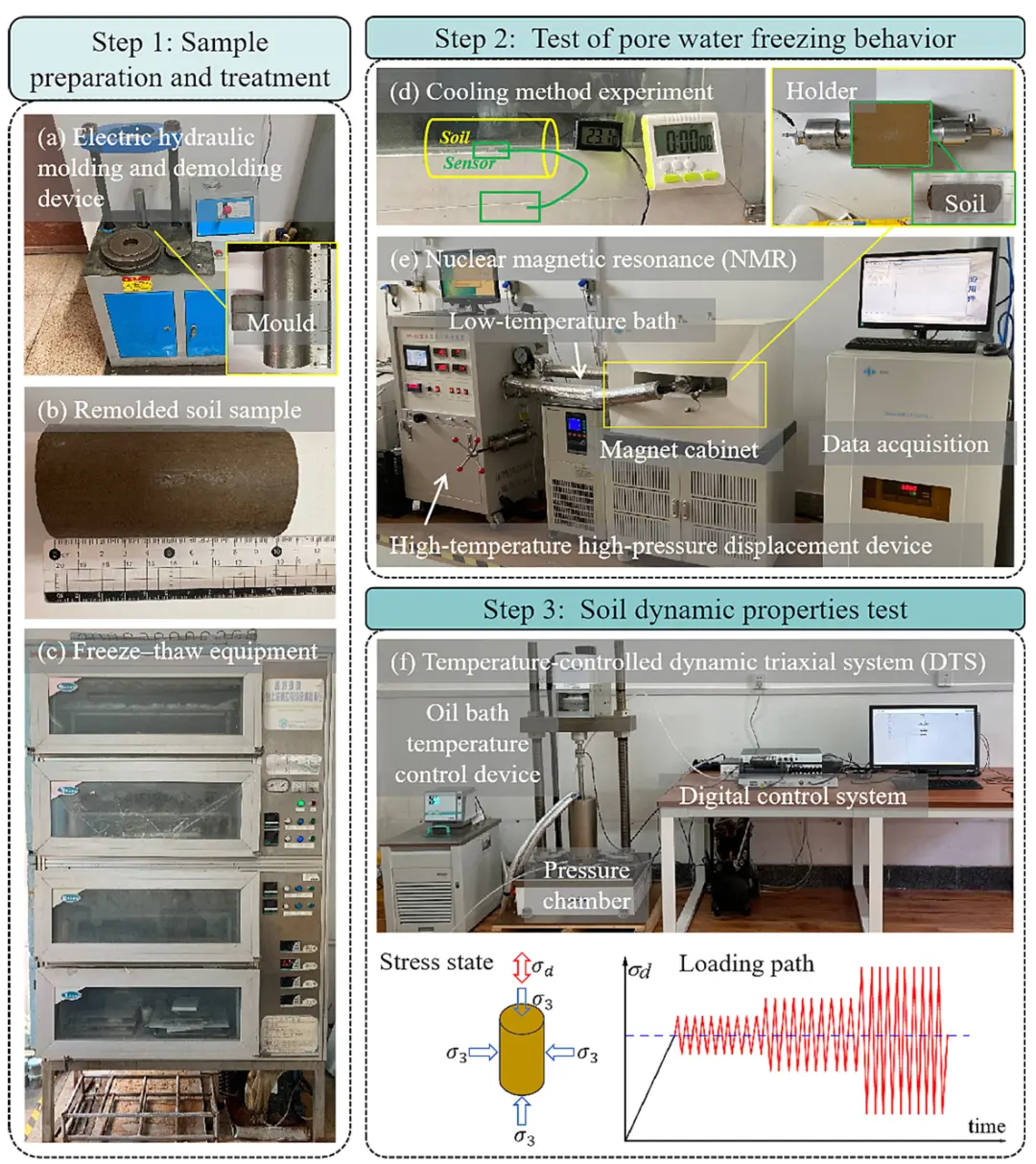
Fig. 3. Diagram of the sample preparation and experimental procedure: (a) electric hydraulic molding and demolding device for soil preparation; (b) remolded soil sample; (c) freeze-thaw equipment; (d) cooling method experiment; (e) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); (f) temperature-controlled dynamic triaxial system (DTS).
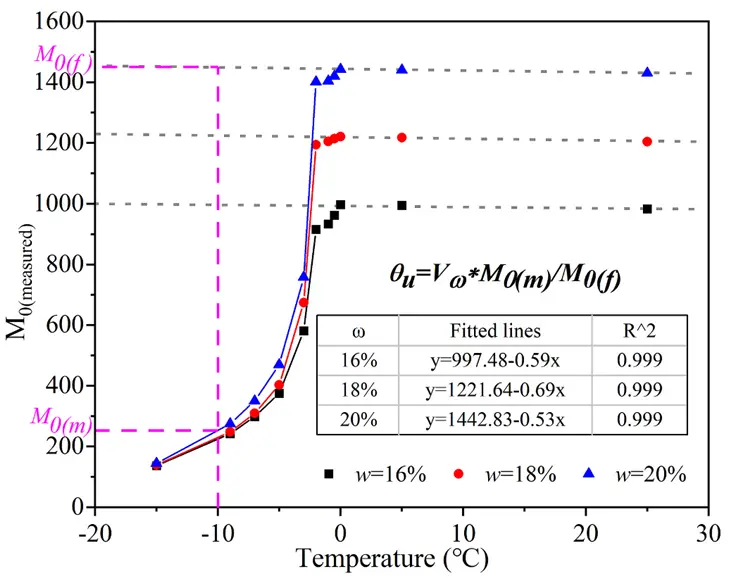
Fig. 4. Calibration of NMR signal amplitude (Mo) in accordance with Curie’s Law
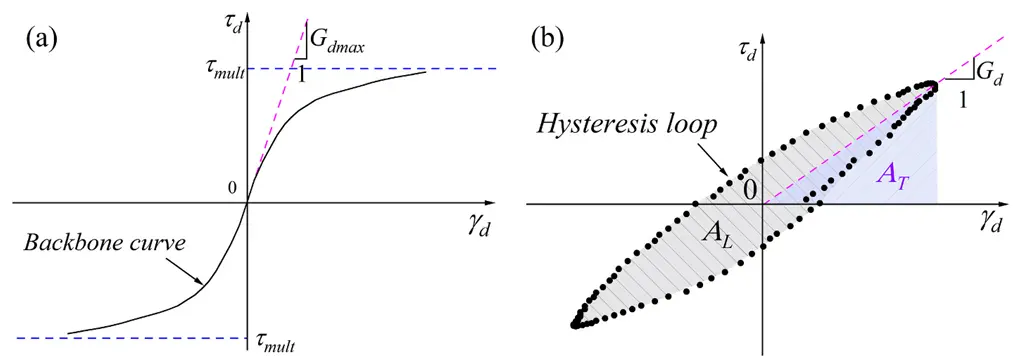
Fig. 5. (a) The basic form of the Hardin-Drnevich hyperbolic model; (b) the calculation of the damping ratio (λ)
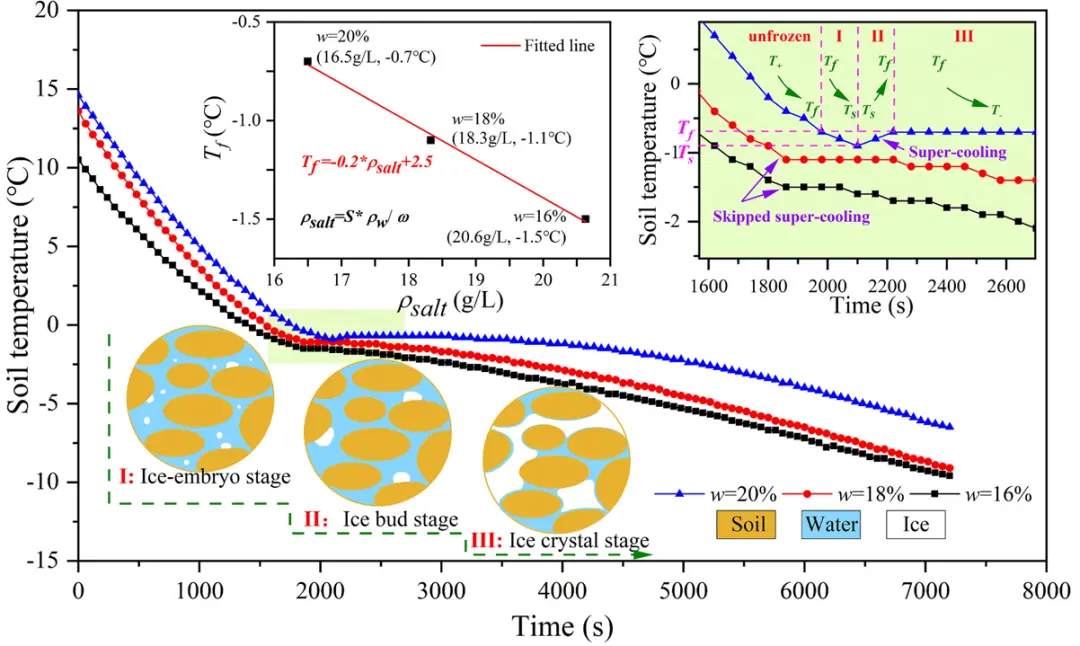
Fig. 6. The cooling curve of soil samples with water contents (w) ranging from 16 % to 20 %.
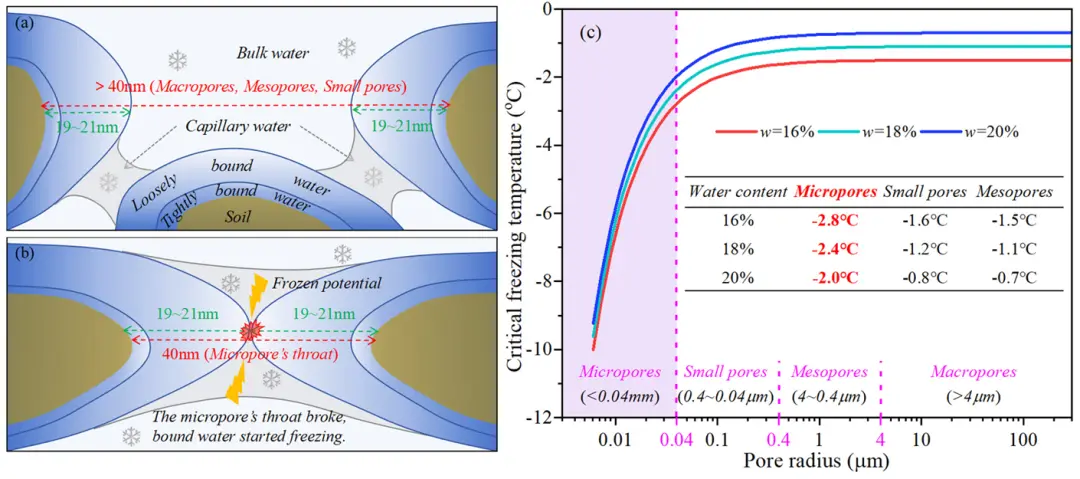
Fig. 7. Freezing of the pore water within (a) Macropores, Mesopores, Small pores; (b) Micropores; (c) critical freezing temperature of pore water in varying pores using the Gibbs-Thomson equation.
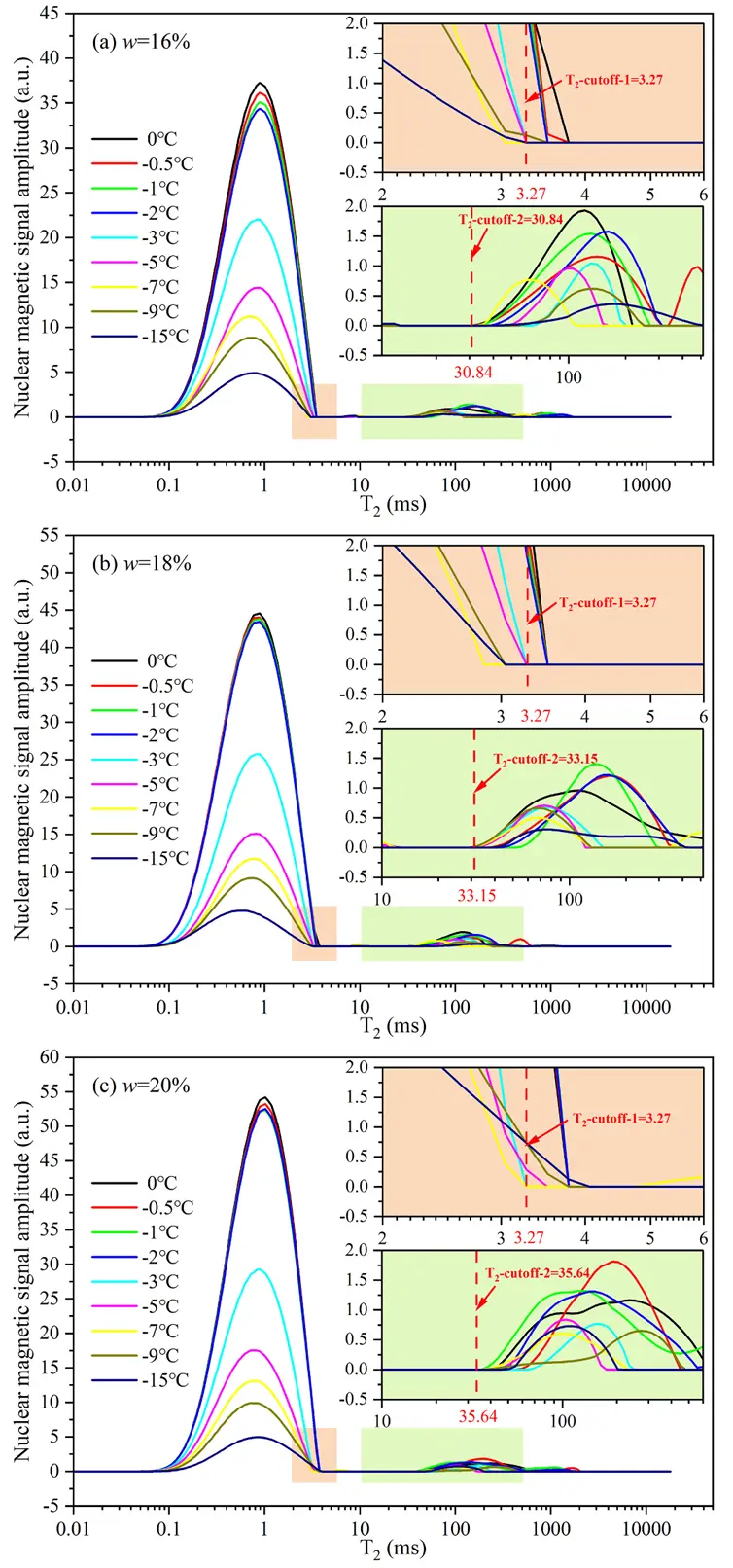
Fig. 8. The T distribution curves of soil samples with water contents (w) of (a) 16 %, (b) 18 %, and (c) 20 % during the freezing process.
Fig. 9. Variations of unfrozen (a) bound, (b) capillary, (c) bulk water contents, and (d) the freezing speed (vf) of bound water in soils with water contents (w) of 16 %, 18 %, and 20 %.
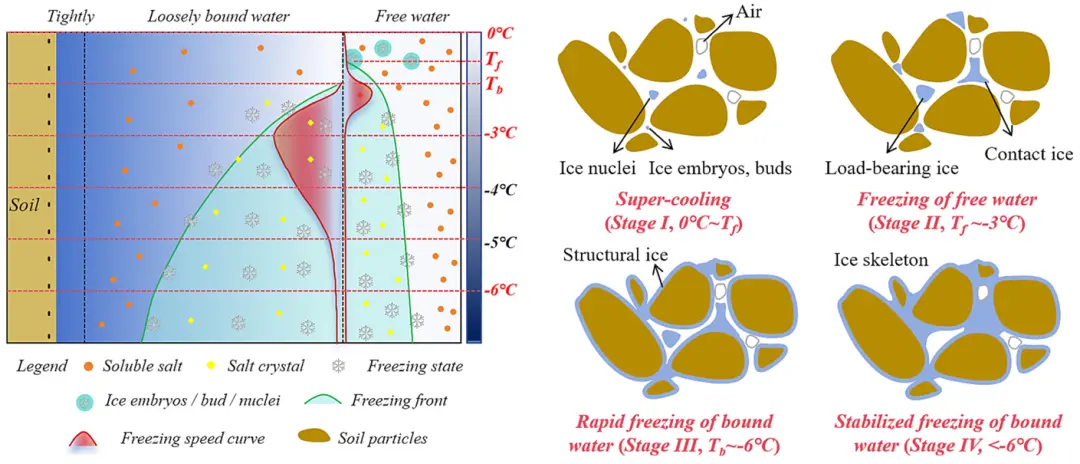
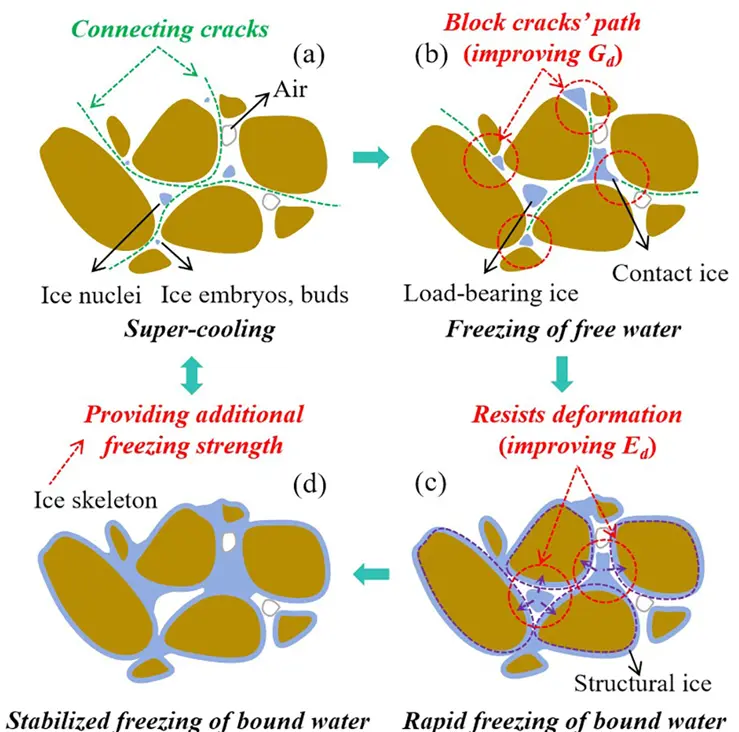
Fig. 10. Schematic diagram of the pore water freezing sequence and the associated evolution of ice skeleton morphology.
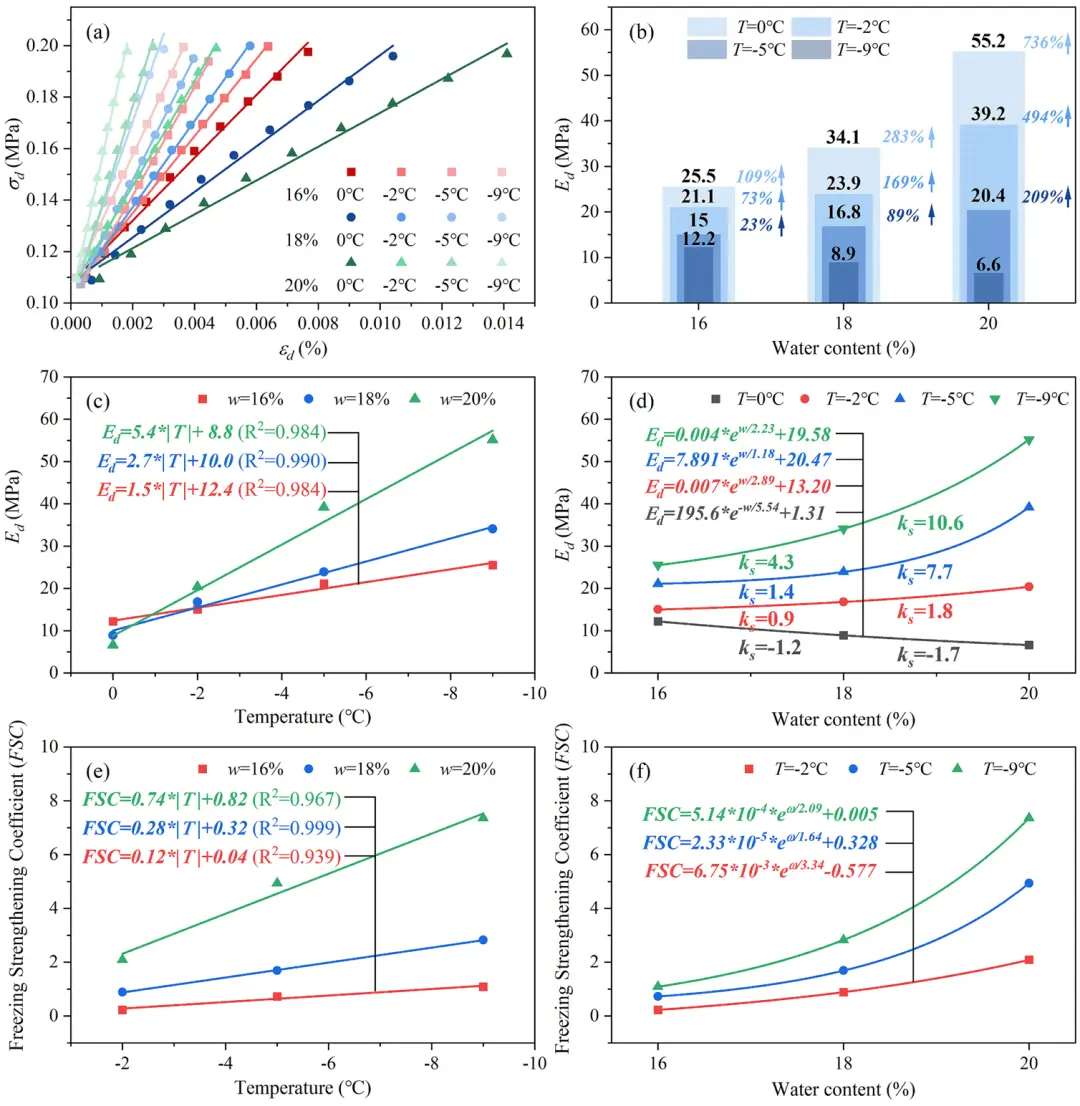
Fig. 11. (a) The stress-strain curves; (b) E of soil samples with different water contents (w) at various temperatures (T); the variations in E with (c) T and (d)w; the variations in Freezing Strengthening Coefficient (FSC) of E with (e) T and (f) w.
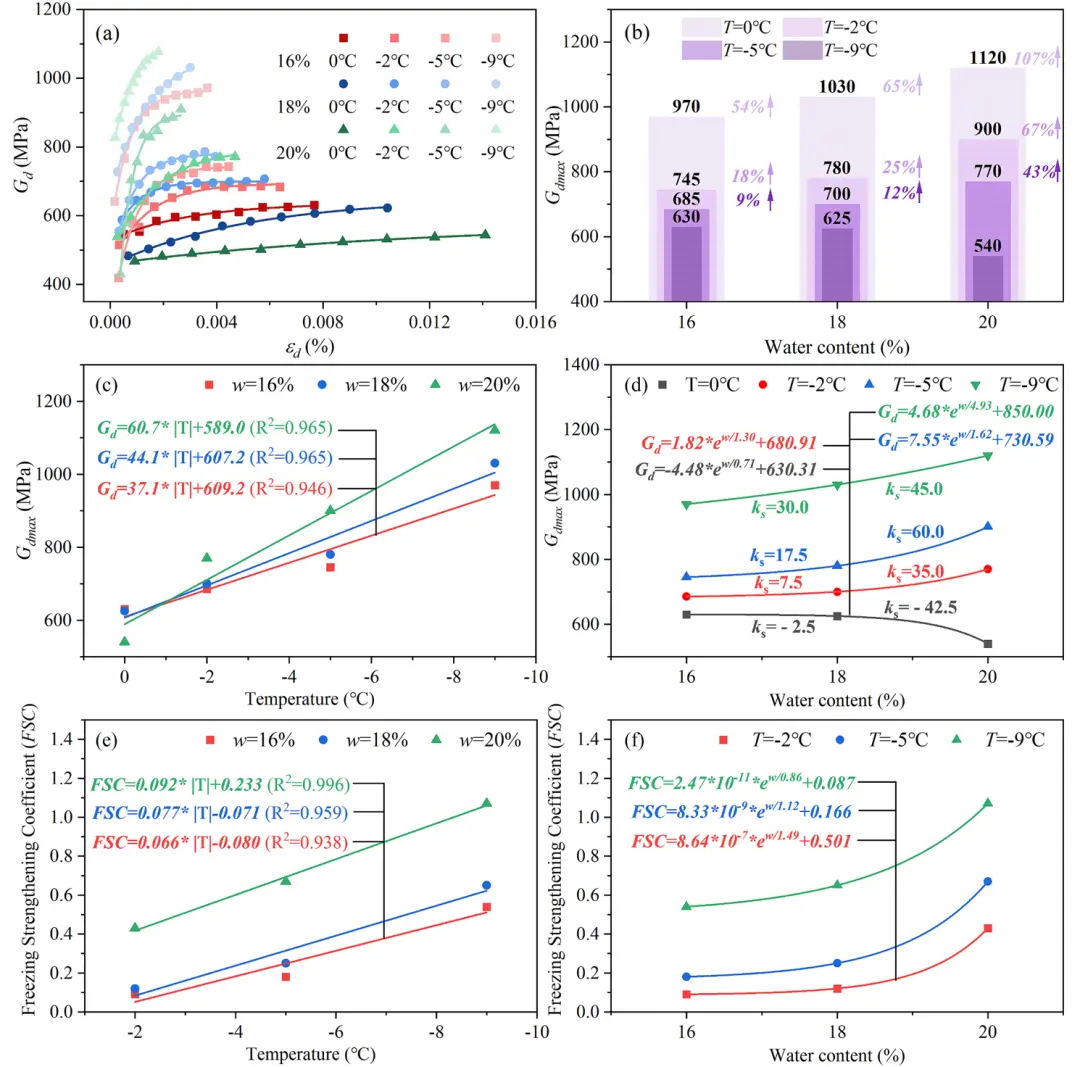
Fig. 12. (a) The variation curves of G with strain; (b) G of soil samples with different water contents (w) at various temperatures (T); the variations in G with (c) T and (d) w; the variations in Freezing Strengthening Coefficient (FSC) of G with (e) T and (f) w.
Fig.13.The variation curves of λ within samples with varying water contents (w) at (a)0 ℃,(b)-2 ℃,(c)-5 ℃,and (d) -9 ℃.
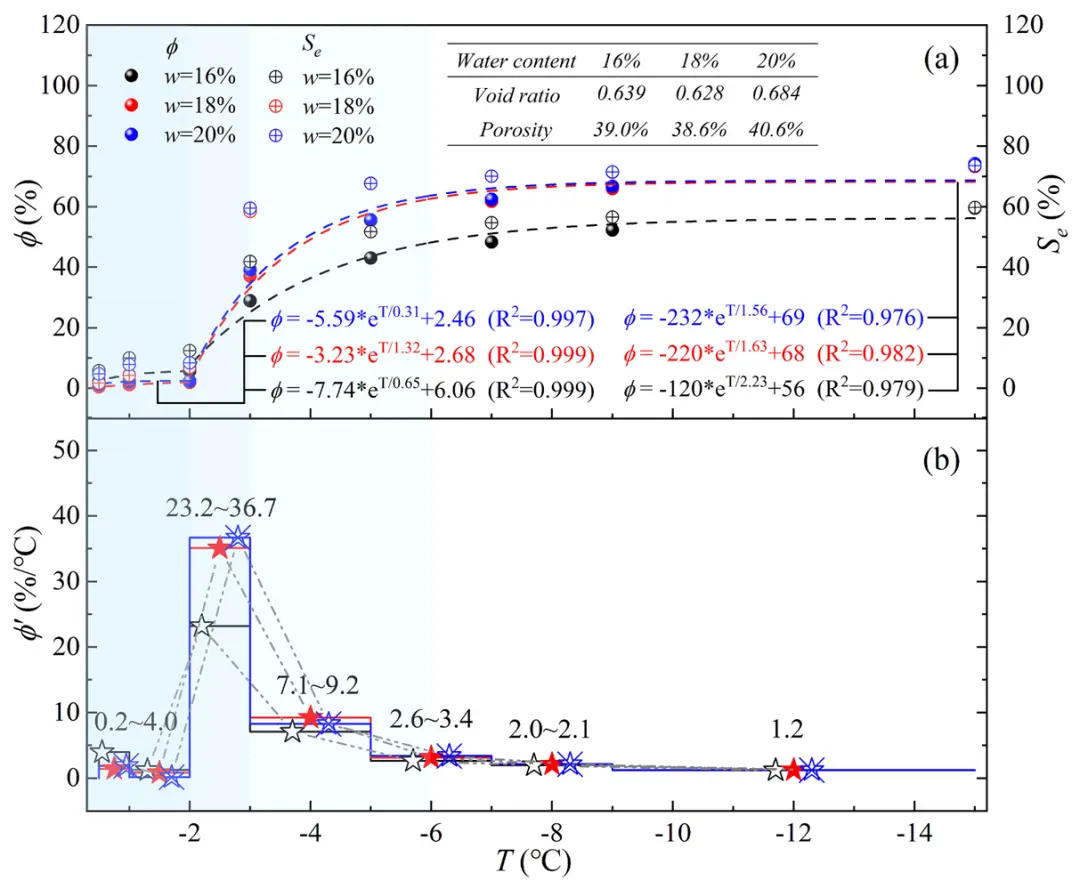
Fig. 14. The variation curves of (a) ice saturation (∅) and relative saturation (S); (b) ice saturation speed (∅) with negative temperature(T).
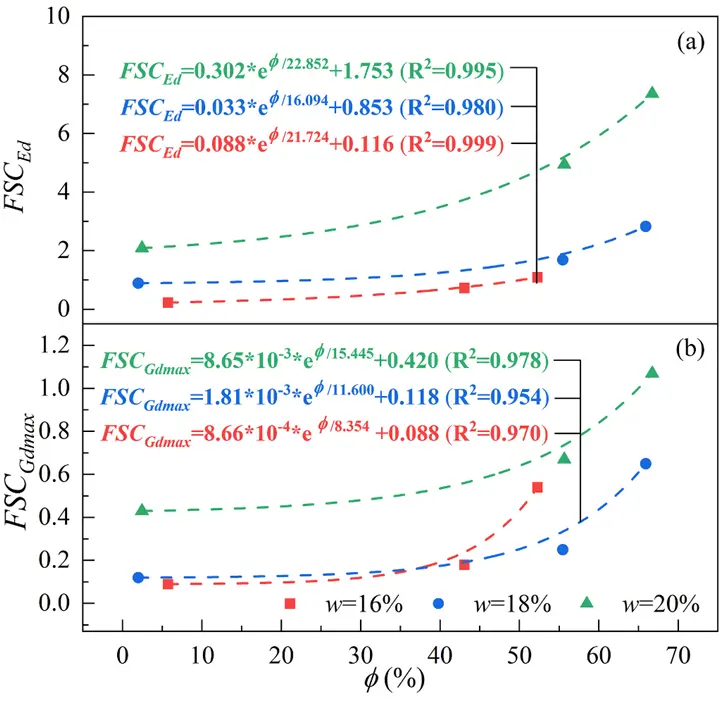
Fig. 15. The variation curves of the Freezing Strengthening Coefficient (FSC) of (a) E and (b) G with the ice saturation (∅) in soils with different water contents (w)
Fig. 16. Schematic diagram of the effect of ice skeleton morphology on the soil's elastic and shear properties during the freezing process.
研究亮点
通过两个T₂截止值识别盐渍土中的孔隙水类型。
结合水、毛细水与自由水冻结后表现出截然不同的力学特性。
孔隙水的冻结顺序决定冰骨架形态及其结构完整性。
基于自由水与结合水的差异冻结行为,提出了新的冻结阶段模型。
盐渍土的动力学参数随孔隙冰饱和度呈指数增长。
GDS动三轴试验系统ELDYN
动三轴系统ELDYN是GDS设备中最经济的动态测试系统,它基于一个高刚度的轴向加载架和横梁上安装的电机作动器。